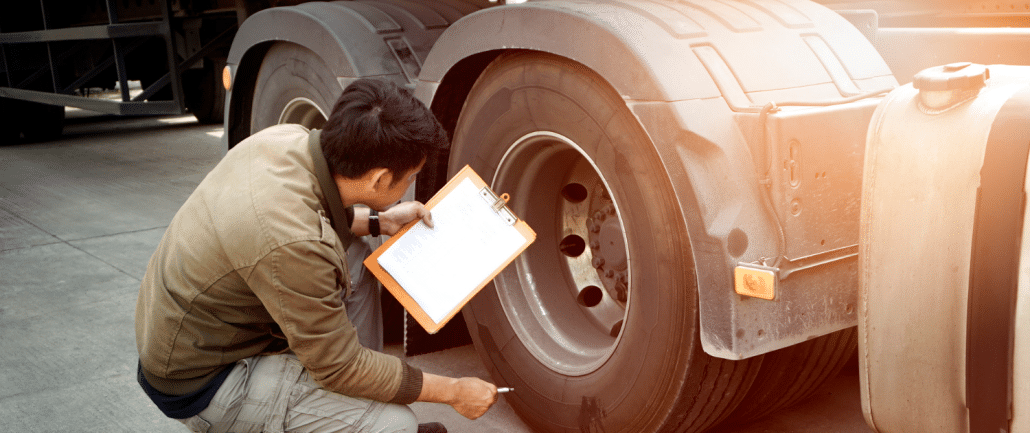
Keeping trucks on the road and running efficiently is one of the most important responsibilities of a fleet manager.
Keeping trucks on the road and running efficiently is one of the most important responsibilities of a fleet manager.
When vehicles break down unexpectedly, the costs go far beyond the repair bill. Missed deliveries, unhappy customers, and downtime for drivers can quickly add up to major losses, which is why having a well-structured fleet maintenance program is essential.
The strongest programs strike a balance between proactive planning and the smart use of predictive technology. Instead of reacting to problems only after they occur, fleet managers can design schedules and systems that prevent most issues before they arise.
Keep reading to discover how to build a strong fleet maintenance program that reduces downtime, lowers costs, and extends the life of your vehicles
Reactive vs. Proactive Maintenance
Reactive maintenance means addressing problems as they come up. For example, replacing a brake system only after it fails or repairing an engine when it overheats. While sometimes unavoidable, this approach can be more costly and unpredictable. Repairs tend to be more expensive because damage has already occurred, and breakdowns often lead to missed work.
Proactive maintenance, on the other hand, is built around regular inspections and scheduled service. Oil changes, tire rotations, brake checks, and filter replacements are planned according to mileage or time intervals. This approach keeps vehicles in top condition, reduces the risk of sudden breakdowns, and makes costs more predictable.
The real strength of a maintenance program comes from creating a system that emphasizes proactive care while leaving room to address unexpected issues quickly and efficiently.
Building a Maintenance Schedule that Works
Designing a schedule that minimizes downtime requires attention to detail and consistency. Fleet managers can start with a few key steps:
- Assess vehicle needs by type and age. Newer trucks may require less frequent service, while older vehicles demand more regular check-ups. Segmenting the fleet helps tailor schedules appropriately.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines. OEM recommendations provide a strong foundation for service intervals and maintenance tasks.
- Incorporate driver feedback. Drivers are often the first to notice unusual noises, vibrations, or dashboard alerts. Building reporting into your program ensures issues are addressed before they worsen.
- Stagger appointments. Instead of pulling multiple trucks off the road at the same time, consider rotating vehicles in and out of service to keep operations running smoothly.
- Track data consistently. Using spreadsheets, maintenance software, or fleet management systems allows managers to monitor trends and predict when service is needed.
A strong schedule balances consistency with flexibility, ensuring vehicles are maintained without disrupting operations.
The Role of Predictive Maintenance Technology
Advancements in technology have made it easier for fleets to take proactive maintenance to the next level. Predictive maintenance uses telematics, sensors, and diagnostic tools to monitor real-time performance and forecast potential issues.
For example, a sensor may detect unusual vibrations in a wheel bearing or a change in oil pressure. This data allows managers to schedule service before the component fails, avoiding costly roadside breakdowns.
Benefits of predictive maintenance include:
- Reduced downtime: Repairs are scheduled at convenient times, keeping trucks on the road when they are needed most.
- Lower costs: Addressing small problems before they grow into major failures prevents expensive repairs.
- Extended vehicle lifespan: Consistent monitoring ensures components are replaced on time, reducing overall wear and tear.
- Improved safety: Early detection of mechanical problems reduces the risk of accidents caused by equipment failure.
By integrating predictive tools into their maintenance programs, fleet managers can move beyond fixed schedules and react dynamically to vehicle performance.
Practical Steps for Fleet Managers
For fleets looking to strengthen their maintenance programs, here are some practical steps:
- Invest in the right technology. Telematics systems and predictive tools vary in cost and complexity. Choose solutions that align with fleet size and budget.
- Train drivers and technicians. Ensure that staff understand how to report data and interpret alerts from predictive systems.
- Integrate maintenance and operations. Connect maintenance schedules with dispatch and route planning to reduce disruption.
- Review performance regularly. Analyze service records, downtime incidents, and repair costs to adjust the program over time.
- Plan for emergencies. Even the best programs cannot prevent every breakdown. Having roadside assistance and backup vehicles available ensures quick recovery when unexpected issues arise.
A well-maintained fleet is about more than avoiding downtime. It creates long-term savings, improves driver satisfaction, and enhances company reputation.
Drivers who know their equipment is safe and reliable are more confident behind the wheel, which can lead to better retention. Customers will also appreciate the timely and reliable deliveries, which strengthens business relationships and your brand identity.
For more ways to stay ahead of the curve in the transportation industry in 2025, be sure to check out the rest of our Employer Blog posts and connect with us on social media.